JS Operators
JavaScript Operators are useful for algorithmic solutions.
1. Addition +
x + y
2. Subtraction -
x - y
3. Multiplication *
x * y
4. Exponentiation (ES2016) **
In mathematics the power operation looks like
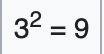
3*3 = 9 Multiplay the main number as many times as the power number is.
x ** y 
5. Division /
x / yDivision operations divides numbers, first number divided by second number.
<script>
let x = 5;
let y = 2;
let z = x / y;
</script>
// output 2.56. Modulus (Division Remainder) %
x % yIn JavaScript the remainder operator returns the number that is not divided, as an example:
<script>
let x = 11;
let y = 2;
let z = x % y;
</script>
// output 1Lets expound this
11 can’t be divided by 2 and be an even number
11/2 = 5.5 this is not modulus solution so then well go an number less
10 is divide by 2
10/2 =5 and still this is not the modulus solution,
The modulus solution is remaining 1, as the initial number was 11
1 is the number left after we were able to divide number 10 by 2.
7. Increment ++
Increment operation means adds one
Postfix increment
y = x++Postfix returns the original value of the variable
<script>
let x = 5;
y = x++;
</script>Output
// y = 5
// x = 6
Prefix Increment
y = ++xPrefix increments the original value of the variable
<script>
let x = 5;
y = ++x;
</script>Output
// y = 6
// x = 6
8. Decrement —
Increment operation means subtracts one
Postfix Decrement
y = x--Postfix returns the original value of the variable
<script>
let x = 5;
y = x--;
</script>Output
// y = 5
// x = 4
Prefix Decrement
y = --xPrefix decrements the original value of the variable
<script>
let x = 5;
y = --x;
</script>Output
// y = 4
// x = 4
Happy Coding !
